Blood pressure is one of the vital signs which tell us how the inner body is functioning. Homeostasis is a phenomenon that can be checked by checking the vital signs and blood pressure is the most important among them.
Understanding the physiology of blood pressure
Blood pressure is by definition the pressure maintained by our heart in the veins. However, blood pressure is not a simple term as it looks here. The pressures in our vessels determine the overall condition of the body. Beginning from the heart to the capillaries at the lowest level, each and every part of our circulatory system has some pressure and each pressure is different from the other pressure. Even the veins and arteries running side by side have different pressures all the time.
Systolic and Diastolic blood pressures
To sum up and make it simple, the blood pressure that we mostly refer to is the systolic and diastolic blood pressure. These are the two basic blood pressures that are mentioned in the general physical examination.
Systolic blood pressure
Systolic blood pressure is the pressure that we measure at the time of active contraction of the left ventricle of the heart. It is the time when blood is actively pumped into the large vessels and then all the peripheral vessels of the body. Systolic blood pressure is for the same reason, a little higher than diastolic blood pressure and it is always written at the top of the equation. The normal range of blood pressure is between 90-140 millimeters of mercury and abbreviated as mmHg.
A systolic blood pressure if higher than 140 mmHg, is considered as high and can be labeled as hypertension if readings are raised on multiple occasions. Systolic hypertension is a term used when only the systolic blood pressure is raised. It occurs with aging because of decreased elasticity of the blood vessels.
Diastolic blood pressure
Diastolic blood pressure is the pressure that is measured at the time of relaxation of the heart. All the deoxygenated blood from the peripheries is collected into the superior and inferior vena cavae and then sent back to the right atrium. Diastolic blood pressure is almost always lower than the systolic blood pressure. There is always a normal difference between two blood pressures which is called mean arterial blood pressure.
Normal diastolic blood pressure is between 60-90 mmHg. Above that is labeled as hypertension. In pregnancy, it is the diastolic blood pressure whose raised values are alarming for the doctor, and prompt intervention is required.
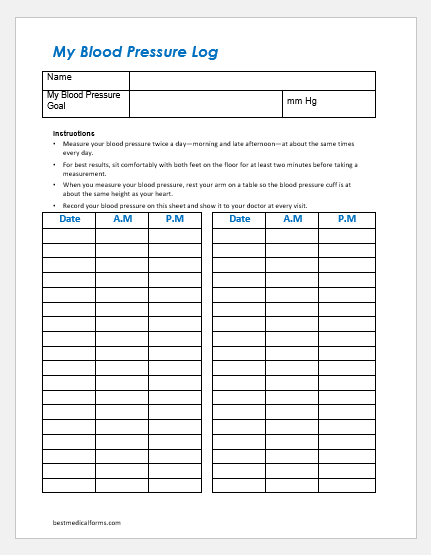
Blood pressure tracking charts
A blood pressure tracking chart is usually used in a patient with hypertension whether in an emergency or not. A wallet-sized blood pressure tracking chart is always kept in the wallet of hypertensive patients because there are high chances of emergency especially if the patient has cardiac issues as well. Systolic and diastolic blood pressures are measured daily to know what the readings are especially to know the efficacy of the anti-hypertensive drug.