The pressure of the blood present in the circulatory system of our bodies is called blood pressure. Blood pressure is achieved by the pumping of the heart in a rhythmic manner where blood reaches out to the major blood vessels and then to small arteries and capillaries.
The blood pressure we measure and refer to is the pressure in the large arteries of the body. Most commonly, blood pressure is measured from the brachial artery. It is one of the vital signs we check in a general physical examination of the patient and assess the general condition.
The blood pressure and physiology of the cardiovascular system
There are two components of blood pressure most commonly measured.
Diastolic and Systolic Blood Pressure
Blood pressure is not just a single entity or a single measurement. It is a set or a ratio of two blood pressures that happen in different phases of a cardiac cycle. These two types of blood pressure are diastolic blood pressure and systolic blood pressure.
Systolic blood pressure
The systolic blood pressure is the numerator in the blood pressure reading. It is the pressure when the left ventricle of the heart pumps its blood into the main vessels. The normal range of systolic blood pressure is 90 to 140 mmHg. A pressure above or below this range is not normal and needs attention and management.
Diastolic Blood Pressure
The diastolic blood pressure is the reading we get when the heart is not pumping blood anywhere. Rather, it is taking the blood from the veins or is almost doing nothing. The normal range of diastolic blood pressure in an adult is 60 to 90 mmHg. Blood pressure less than that or more than 90 needs to be evaluated.
Causes of High Blood pressure
A number of reasons result in high blood pressure commonly known as hypertension. They depend upon the age, gender, lifestyle, and certain other factors.
- More than half of the population suffering from hypertension is due to unknown reasons. This is typically called essential hypertension.
- Then there is secondary hypertension which occurs always due to some underlying pathology. For example, almost all chronic and acute renal diseases cause raised blood pressure.
- Some Adrenal gland tumors, congenital and some acquired diseases result in high blood pressure because glucocorticoids and especially mineralocorticoids take an active part in blood pressure control.
- Pregnancy-induced hypertension is yet another reason.
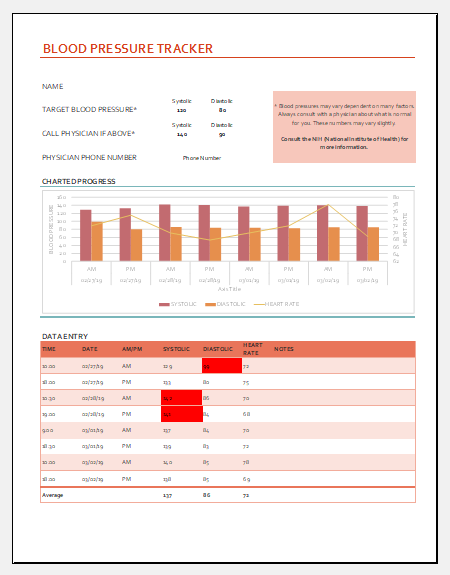
Blood Pressure tracking chart
So, whatever the underlying cause of raised blood pressure, a proper record has to be maintained to establish the diagnosis and plan the management.
They say, sometimes only keeping a record can help in controlling blood pressure. So, these tracking charts can be used at home as well.
In the chart, we mention the date, time, and readings of systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
Preview