COPD is an acronym for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. It is a group of obstructive lung diseases that affect our respiratory system, which differs from the restrictive diseases of the lungs. Emphysema and chronic bronchitis are the two types that are included in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Definition of COPD
According to the World Health Organization, COPD is a group of lung diseases characterized by chronic obstruction of the lung’s airflow. This chronic obstruction interferes with normal breathing, and the disease is not fully reversible. If not diagnosed in time, COPD can prove to be a life-threatening lung condition.
Causes of COPD
Several factors cause chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases. However, smoking is the most common cause of chronic bronchitis. People who are in the habit of smoking in any form are at a higher risk of developing the disease than non-smokers.
Some non-smokers with congenital deficiency of alpha-one antitrypsin in their bodies suffer from the COPD disease called emphysema.
Other causes of COPD are exposure to fumes and gases, second-hand smoke in the form of pollution, passive smoking, dust, fumes, etc.
Symptoms and diagnosis of COPD
The signs and symptoms of COPD are very distinctive. It is said that if COPD is underdiagnosed, it can prove fatal for life. There is a term called “smoker’s cough.” A smoker’s cough is specific to chronic bronchitis.
Pink and blue puffers are used for patients with emphysema and chronic bronchitis, respectively. The symptoms begin with a cough and mild shortness of breath, which progresses and sometimes happens with exertion.
Cough is the most prominent feature of COPD. It is always productive, and a copious amount of mucus is produced. To be labeled with COPD, a patient must suffer from this cough for three consecutive months, and these episodes must happen within two years. Coughing is sometimes so severe that it results in rib fractures or the patient loses consciousness for a while due to a prolonged interruption in oxygen supply.
The rest of the diagnosis is made by clinical examination. On chest auscultation, a wheeze is present that doesn’t clear after coughing. With time, extreme coughing results in a barrel-shaped chest, which can be seen clinically.
Advanced stages of chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases result in cor pulmonale, and heart function is also compromised as a result of cor pulmonale, swollen legs, bulging neck veins, and depression result.

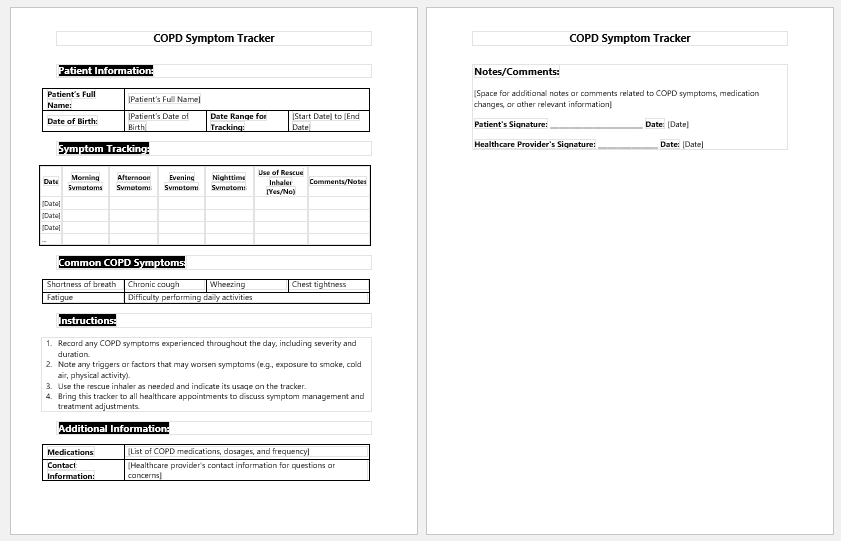
COPD symptom tracker
The COPD symptom tracker is a Performa used to establish the diagnosis of the disease. Since we cannot label every coughing patient as having COPD, we need to track the patient’s symptoms to develop the diagnosis firmly.
The most important parts of the form are the patient’s name, sex, age, and occupation. The patient’s smoking history is asked because COPD is strongly associated with smoking. The main symptoms are then added in the columns, and their frequency is noted over weeks and months.
- Nursing Documentation Templates
- Letters for being Unfit to Travel
- Mental Health Evaluation Forms
- Forms Used by Pediatricians
- Various Forms Related to Pregnancy Verification
- Common Forms Used by ENT Specialists
- Patient Registration Confirmation Messages
- Quotation Letter for Medical Services
- Mental Health Letter by Doctor
- Excuse Letter for Absence due to Medical Checkup
- Response Letter to Feedback on Improvement in Hospital
- Letter to a Mother Who Miscarried
- Patient Feedback Letter Complaining on Issues or Incidents
- Letter to Family about Miscarriage
- Patient Constructive Feedback Letter for Quality Care Improvement