Parkinsonism is a brain disease. It is graded clinically as a syndrome because it involves several symptoms and signs due to the brain’s pathology. Parkinson’s disease is considered a syndrome, with its clinical symptoms showing in a classic triad of Bradykinesia, tremors, and rigidity.
Clinical Features of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease is very well known for its symptoms and is classically diagnosed based on signs and symptoms.
Tremors
Tremor is the most common symptom of the disease. The disease typically shows resting tremors, in which the patient shows tremors in the limbs at the time of resting arms. They are visible when the patient rests his arms on his lap or lies on the bed. Resting tremors are sometimes referred to as Parkinson’s tremors.
Hypokinesia
Hypokinesia and Bradykinesia are other signs of Parkinson’s disease. Bradykinesia is the slowness of the movement, and hypokinesia is the decrease in spontaneous movement. They occur due to pathological changes in the brain’s basal ganglia.
Postural instability
Due to tremors and Bradykinesia, postural instability naturally appears in Parkinsonism patients. This leads to frequent falls in patients with Parkinsonism.
Rigidity
Muscle tone is increased abnormally, and the patient shows stiffness and rigidity in the joints. A typical name used for Parkinsonism is “cogwheel rigidity.”.
Causes of Parkinsonism
- Some medications are known to cause the disease in about 7% of cases of Parkinsonism. Antipsychotic drugs, lithium, and tetrabenazine are notorious for causing Parkinsonism. The incidence of disease increases if the drug-taking individual has reached old age.
- Certain toxins are also responsible for causing pathology in the basal ganglia and resulting in Parkinsonism. Chronic and excessive manganese is also known to be one of the causes of the disease.
- Infectious agents like HIV/AIDS and encephalitis lethargica also cause the symptoms of Parkinsonism.
- Direct injury to the brain, for example, during boxing, results in chronic traumatic encephalopathy. It is also called Boxer’s dementia.
- Some vascular injuries or diseases of the brain also result in the manifestation of Parkinsonism.
Treatment of Parkinsonism
A multidisciplinary and broad-based approach is required for managing Parkinsonism. Management begins with counseling the family about the disease’s disclosure, manifestations, and treatment options. The aim is to improve the quality of life and the gradual recovery of symptoms with time. Medications are used in the treatment, supported by physiotherapy, and other disciplines are also involved. Levodopa is the drug of choice, supported by other drugs like MAO inhibitors.
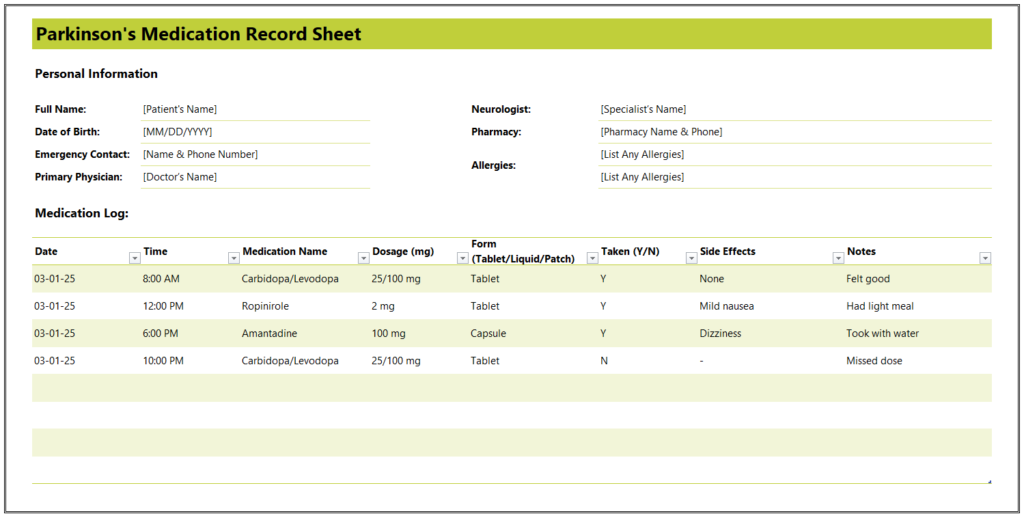
Parkinsonism medication log
Treatment of Parkinsonism takes time and requires regular administration at the proper dose. This is only possible if caregivers maintain a tracking chart or medication log. Sometimes, the drug dose has to be tapered off, which again needs a record. The Parkinsonism medication log works on the same principles as other medication logs, in which the date and time of the drug are mentioned along with the proper dose and any effects, if visible.
- Nursing Documentation Templates
- Mental Health Evaluation Forms
- Forms Used by Pediatricians
- Various Forms Related to Pregnancy Verification
- Common Forms Used by ENT Specialists
- Pain Diary Worksheet Template
- Forms Commonly Used by Old Age Homes
- Medical Treatment Consent Form
- Home Exercise Program Worksheet
- Forms Used for Mental Health Assessment
- Forms Used by Psychologists
- Medical Forms Commonly Used by/for Students
- Assessment Consent Form
- Forms Used by an Anesthesiologist
- Not Fit to Fly Certificate Template